我只能一个一个工具去学习,去安装有从源码安装也有直接使用apt进行安装,再去看man,去google关于这个工具的document,开始对tutorial,getting started xxx或example进行系统性的学习和分析,然后掌握工具的使用,以及与其他工具进行配合使用等,这可能是最笨的方法了。
前提条件,需要预先安装一些包用于编译: #sudo apt-get install git help2man perl python3 make autoconf g++ flex bison ccache #sudo apt-get install libgoogle-perftools-dev numactl perl-doc #sudo apt-get install libfl2 # Ubuntu only (ignore if gives error) #sudo apt-get install libfl-dev # Ubuntu only (ignore if gives error) #sudo apt-get install zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev # Ubuntu only (ignore if gives error)
git clone https://github.com/verilator/verilator # Only first time
# Every time you need to build: unsetenv VERILATOR_ROOT # For csh; ignore error if on bash unset VERILATOR_ROOT # For bash cd verilator git pull # Make sure git repository is up-to-date git tag # See what versions exist # 这里的版本与 文档保持一致,v5.008 git checkout v{version} # Switch to specified release version
tar -xzvf systemc-3.0.1.tar.gz 2. 进入systemc目录并创建临时目录objdir ```bash cd systemc-3.0.1 mkdir objdir cd objdir
配置
1 2 3 4 5
../configure or ../configure 'CXXFLAGS=-std=c++17' or ../configure --prefix=/usr/local/systemc-3.0.0
编译
1
make
编译和运行子文件夹中的案例
1
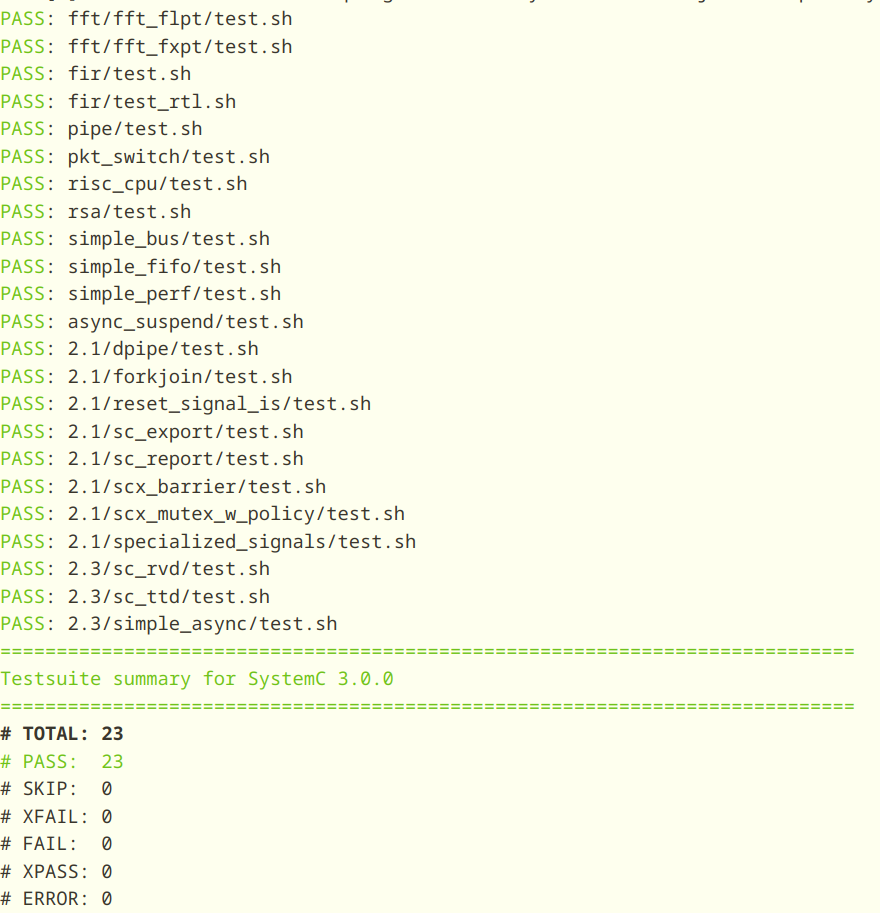
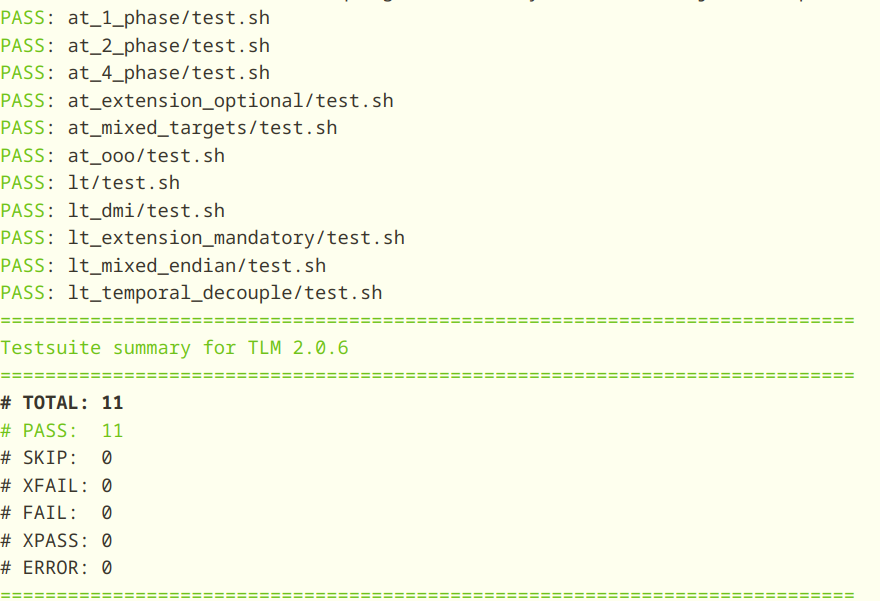
make check
#include<stdio.h> intmain(int argc,char* argv[]){ puts("hello world!"); puts("happy new year!"); puts("good good study, day day up!"); puts("路曼曼其修远兮,吾将上下而求索"); puts("萧瑟秋风今又是,换了人间"); return0; }
int fputc(int c, FILE *stream);
int putc(int c, FILE *stream);
int putchar(int c);
int fputs(const char *restrict s, FILE *restrict stream);
int puts(const char *s);
DESCRIPTION fputc() writes the character c, cast to an unsigned char, to stream.
putc() is equivalent to fputc() except that it may be implemented as a macro which evaluates stream more than once.
putchar(c) is equivalent to putc(c, stdout).
fputs() writes the string s to stream, without its terminating null byte ('\0').
puts() writes the string s and a trailing newline to stdout.
Calls to the functions described here can be mixed with each other and with calls to other output functions from the stdio library for the same output stream.
For nonlocking counterparts, see unlocked_stdio(3).
RETURN VALUE fputc(), putc(), and putchar() return the character written as an unsigned char cast to an int or EOF on error.
puts() and fputs() return a nonnegative number on success, or EOF on error.
#include<stdio.h> intmain(int argc,char* argv[]){ puts("hello world!"); puts("happy new year!"); puts("good good study, day day up!"); puts("路曼曼其修远兮,吾将上下而求索"); puts("萧瑟秋风今又是,换了人间"); puts("仰天大笑出门去,我辈岂是蓬蒿人"); return0; }